How do you stick to your New Year’s resolutions? That was the behavioural design challenge 65 SUE Fundamentals Course alumni tackled at the beginning of the year.
For two months, we coached them to reach their goals and build new habits. Because we know that breaking a habit is hard. But with our new LAST framework, we made it work!
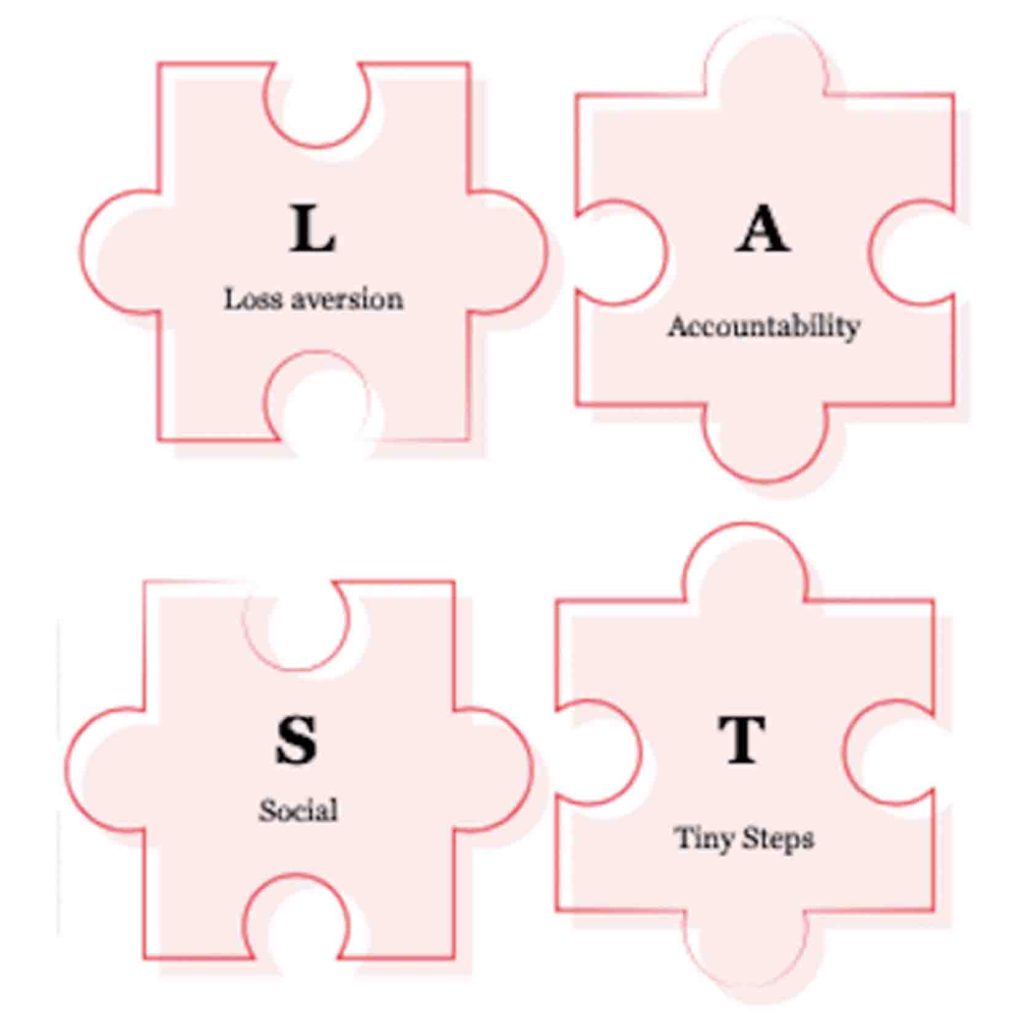
New LAST Framework
Resolutions have everything to do with creating new habits or beating old ones. But changing habits can be a difficult task. That is why we have created a brand new framework.
“How to make habits LAST”.
Every letter stands for a principle you should apply in practice: Loss aversion – Accountability – Social – Tiny steps.
You will be amazed at how four easy questions can effectively change your habits. We’ve done the ultimate behavioural design challenge to prove that it works! You can download the cheatsheet here.
But first, let’s start with defining the desired behaviour.
The Behavioural Statement
Everybody first needed to formulate a New Year’s resolution to start the challenge. We saw all kinds of goals coming through:
- Plan more dates
- Read more books
- Paint more
- Sleep better.
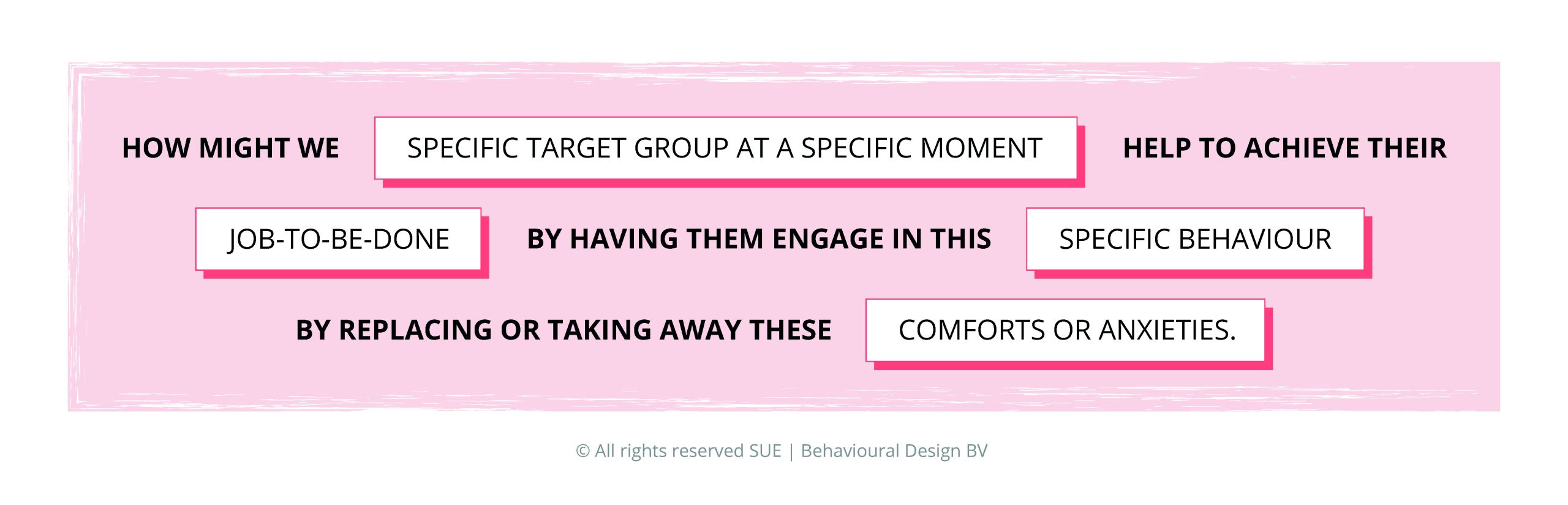
But what is more? And what does better sleep mean? When you want to change your habits, it is important to break down the desired behaviour into very concrete actions and goals. Thinking about your specific behavioural statement can help with that!
“How might we specific target group at a specific moment help to achieve their job-to-be-done by having them engage in this specific behaviour by taking away comforts or anxieties”.
The target group was evident because they wanted to change their own behaviour. But picking a specific moment or a specific behaviour was very important to think about. When focused on this statement, the resolutions already became more concrete.
- Organize 5 dates this year with my wife.
- Go outside for at least 45 min a day.
- 3 times a week work 1.5 hours on my physical health in the gym.
It’s also essential to think about your job-to-be-done. Why do you want to read/paint/walk/date more? The overall theme we saw was that everybody wanted to become happier in 2023 and that those behaviours would help them achieve that goal
Not sure yet what your specific goals will be to become happier this year? You can also read our blog about our 5 behavioural design interventions to achieve happiness this year.
As you will see, the LAST framework will also focus on removing comforts from your current behaviour by adding loss aversion to the process. Moreover, it will help them engage in their specific behaviours by implementing tiny steps or help them make their goals social. Now let’s look at every step of the framework in more detail.
Download the LAST framework cheatsheet
Do you struggle with building new habits? We all know creating new routines can be difficult. That is where Behavioural Design can help you out. We’ve created a new tool with four easy questions to answer to help you build new habits. This cheat card will help make your habits LAST!
1. LAST: Making it Social
One of the steps the LAST framework provides is making it Social. It can be a good starting point when creating a new habit. When you have thought about your desired behaviour and made it very specific in your head, it is time to make it social. Write down your new desired behaviour on paper or announce it publicly. It is a mind trick that works wonders. That is because our mind loves consistency. If we say we will do something, we want to stick to this behaviour to appear consistent (even if we write it down for ourselves).
Another way to add a social aspect is by setting yourself up for positive feedback. Engage your social network for them to give you compliments and cheers. This will trigger positive emotions that help stick to the new behaviour. If something feels good, you are inclined to keep on doing it.
2. LAST: Tiny steps
When are you going to perform the behaviour?
It is a crucial step to think about when you want to change your behaviour. You have to ‘spark’ the behaviour at the right time. Therefore, the next section we dive into from the LAST framework is Tiny steps.
The key to creating new habits is by starting small. Little steps will build up exponentially. Creating a new habit is difficult, so don’t design for disappointment by making the change too big.
You can make it easier by connecting the new behaviour to the existing behaviour. Our brain will reprogram more quickly if we build upon our current routine. For example, say you’ll drink a glass of water every time you have washed your hands after a toilet visit.
Try it for yourself: Every time I … I will …
This is what we call tiny steps in behavioural design. It is a powerful method to get you started with behaviour change without getting overwhelmed by the task that you are facing.
3. LAST: Loss aversion
When you look at the behavioural statement, finding a way to take comforts or anxieties away is vital. Why would you go to the gym if you feel comfortable on your couch and there are no direct consequences if you don’t go? You can make up an excuse for yourself not to go when no strings are attached. The LAST framework will help you set some consequences when you don’t perform the behaviour. We are going to implement loss aversion to help you achieve your goals.
Because if you put something at stake that you don’t want to lose, it will drive your willingness to change. We humans simply don’t like losing something; therefore, it will activate our loss aversion.
For example, commit to donating money to a charity you don’t like. Or promise your partner you will cook for a month if you don’t keep up with your new habit. As long as it is something you dislike to do or lose, you design a context in which you want to sustain the desired behaviour and lose your current bad habits.
One important thing to add: Make sure it is something you actually can do in case you fail to stick to your new habit. If you are unable to do your ‘punishment’, it won’t motivate you to stick to your goals.
Do you want to be part of the next behavioural design challenge?
We offer multiple FREE opportunities for all SUE alumni who followed the Fundamentals Course. Attend a hackathon, join a behavioural design challenge like this one or ask your personal questions about social psychology in our alumni group. Read our brochure and sign up now for the course.
4. LAST: Accountability
To finish the entire framework, we are now looking at the final step of the LAST framework: Accountability.
Changing a habit on your own can be difficult. Therefore, finding someone who can keep you accountable for your behaviour can be helpful. Tell them to check on you once a week. What counts is the thought of social pressure. It makes us want to stick to a behaviour.
Also, by adding accountability, you design a context in which you can lose face by not living up to your intentions.
Asking someone to help you achieve your goals is already taking some sort of action. That is why it is important to answer these questions for yourself:
- Who are you going to ask?
- When are you going to ask?
- When should they check on you?
When you are determined to reach your goal, involving someone to keep you accountable can be a great tool to keep you motivated!
How to make habits LAST: example
Now that you understand the LAST framework, it is time to put it into practice. Nothing can convince us more than social proof. We have just that from our group that tackled this challenge themselves.
We highlighted one resolution of a member of this group that might be useful for many people:
” I want to put my desk up in a standing position during every online meeting”.
You might have heard of a convertible desk. You can easily lift up the desktop to sit less during the day. But the habit of actually converting it is challenging to create. It is the perfect example to apply the LAST framework on.
- Tiny Steps: Connect the new behaviour to existing behaviour. Whenever you plan a virtual meeting (current behaviour), you will schedule an additional reminder before the start of the meeting to convert your desk into a standing position (desired behaviour).
- Accountability: Let the person you are meeting with know in advance that you have the resolution to stand up. For example, when you send an invite, put it in the description of the meeting. The social pressure of them asking you about it will motivate you to stand up.
- Loss aversion: What is something you absolutely don’t want to do if you fail to achieve your goal? For example, turn your desk away from the window, no more coffee allowed that day, or your entire salary of that day goes to an organisation you don’t like. Pick something you don’t want to do and promise to stick to it.
- Social: Announce your resolution. For example, tell everybody in your office, your partner at home or write it down for yourself. Our mind loves consistency. If we say we will do something, we want to stick to this behaviour to appear consistent.
What do you think? Would these steps help you to stand up more during the workday?
In conclusion
We are very happy to see so many enthusiastic people who put our new framework into action. Now it is your turn to tackle your goals or resolutions this year. Changing behaviour is complex. But with these four easy steps, you can start making a difference this year and reach your goals!
Astrid Groenewegen – Behavioural Design Academy
How do you do. Our name is SUE.
Do you want to learn more?

Suppose you want to learn more about how influence works. In that case, you might want to consider joining our Behavioural Design Academy, our officially accredited educational institution that already trained 2500+ people from 45+ countries in applied Behavioural Design. Or book an in-company training or one-day workshop for your team. In our top-notch training, we teach the Behavioural Design Method© and the Influence Framework©. Two powerful tools to make behavioural change happen in practice.
You can also hire SUE to help you to bring an innovative perspective on your product, service, policy or marketing. In a Behavioural Design Sprint, we help you shape choice and desired behaviours using a mix of behavioural psychology and creativity.
You can download the Behavioural Design Fundamentals Course brochure, contact us here or subscribe to our Behavioural Design Digest. This is our weekly newsletter in which we deconstruct how influence works in work, life and society.
Or maybe, you’re just curious about SUE | Behavioural Design. Here’s where you can read our backstory.