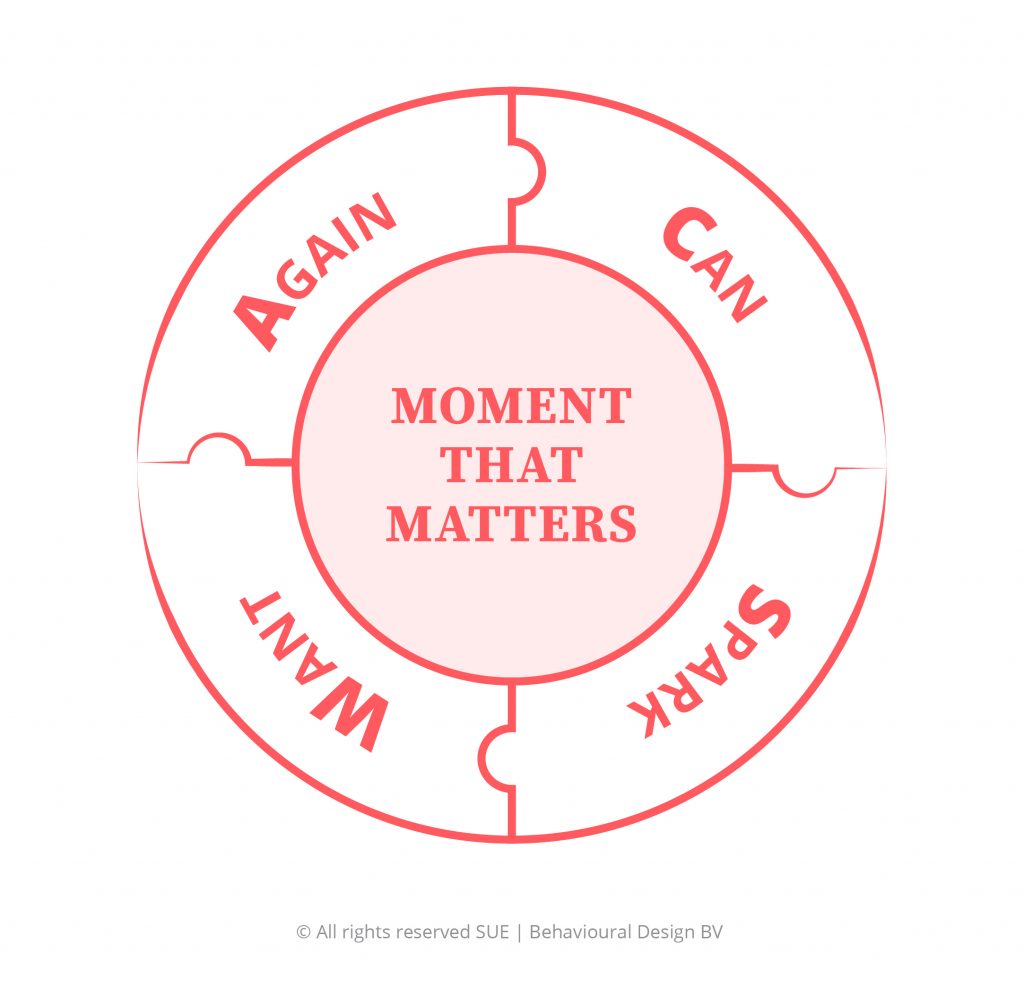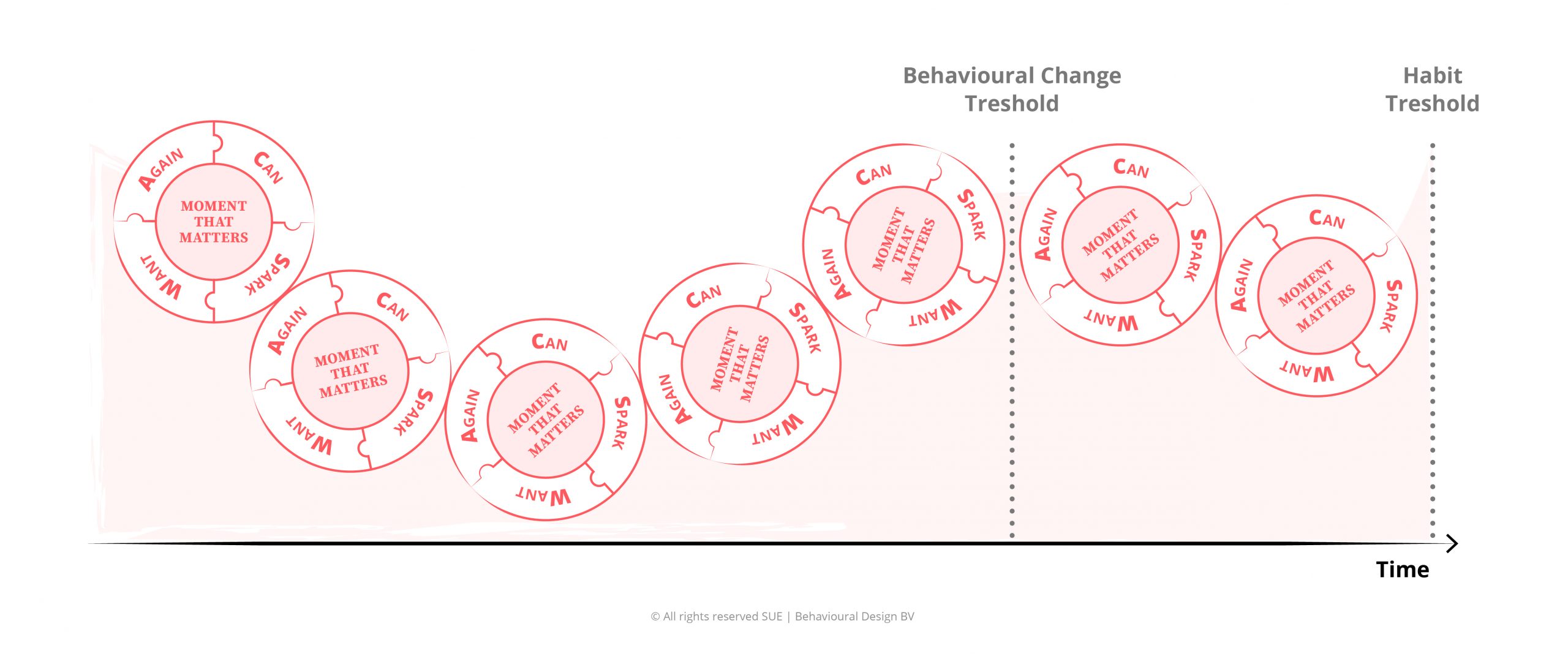
The SUE | Influence Framework© is a powerful mental model we developed at SUE to analyse the forces that shape behaviour systematically. The framework will provide you with all the human insights you need to develop ideas for behavioural change. A deeper understanding of the forces that prevent people from change or boost behavioural change is essential to influence minds and shape behaviour. In this blog post, we explain the model step-by-step and illustrate it with lots of examples.
1. How does influence work?
For a complete overview of the essence of behavioural design, I want to urge you to read our blog “What is behavioural design“. For this blogpost, it suffices to understand that you need three ingredients for successful behavioural change:
- Understand how people think and how they make decisions. (cognitive psychology)
- Know how you can analyse the forces that shape people’s behaviour (SUE | Influence Framework©)
- Learn how you can come up with ideas for behavioural change
One of the biggest misconceptions of behavioural design is that it’s limited to this third ingredient. Think about all the persuasion techniques in the field of interface design and UX to boost online sales. Booking.com has turned these techniques into an art form.
However, if you don’t consider what happens inside the human mind you try to influence, you can use as many persuasion tactics as you want; you’re not going to be successful.
Let me illustrate this with an example: You can use all the scarcity, authority, social proof in the world to persuade me to make my next city trip with Flixbus. But as long as you haven’t addressed my (probably irrational) prejudice that travelling by bus coach will be a social nightmare, full of annoying people, my brain will stay locked for every attempt to change my behaviour.

2. The forces that shape behaviour
You will understand why people do the things they do and what prevents them from changing their behaviour.
Understanding these forces helps you to spot opportunities for behavioural change. Only when you have armed yourself with these opportunities you can start to come up with ideas.
To illustrate this with the example from above. Only when you consider that I have anxieties, doubts and prejudices that prevent me from travelling by coach will you have the proper insight to come up with ideas to influence my decision-making. You will ask yourself how we might take away the prejudice that cheap coach travel equals a social nightmare.
If you want to design a successful strategy for behavioural change, you will have to work outside-in. You start with learning what happens inside people’s minds, and you adapt your intervention to this understanding.
Would you like to power up your team or project with behavioural intelligence?
Feel free to contact us. We are happy to tell you more about our consultancy or academy. Helping you innovate, transform or grow levering insights from behavioural science in practice.
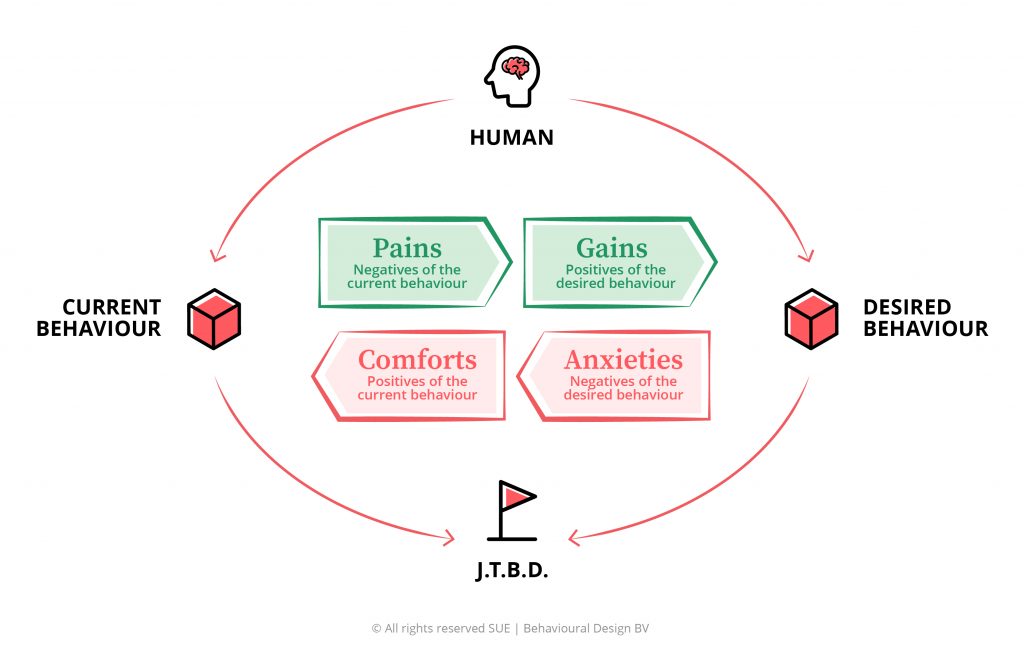
The SUE | Influence Framework© has three parts, with a total of seven elements. We will delve into these three parts below.
- Part 1: Current and Desired Behaviour
- Part 2: The Job-to-be-Done
- Part 3: Pains, Gains, Comforts and Anxieties
3. Current and Desired Behaviour
The best way to think of behavioural change is that you need to have someone (or yourself) switch from a current to desired behaviour. This sounds obvious but is actually quite challenging. Because people need to stop doing the things they do and start doing something new. Stopping is hard because your current behaviour is full of comforts. You don’t need to think about it, and your behaviour is more than often driven by habits that are difficult to control.
Furthermore, there are several difficulties associated with new behaviour too: Am I able to do this? Do I want it? Do I trust it? Do I get it? Can I afford it? What will others think of me?
You immediately sense that, if you want to get someone from A to B, you will have to deal with several forces at work that lock us in our current behaviour and prevent us from switching to the desired behaviour. The SUE | Influence Framework© is nothing more or less than a tool to uncover these forces.
4. The Job-to-be-Done
If you want to understand why people do the things they do, then the Job-to-be-done framework by Clayton Christensen is essential. In a famous Harvard Business Review paper, Christensen argues that people “hire products and services” for a job that arises in their life. Understanding the “job” or “task” is the key to understanding what motivate people to do the things they do. If you want to know how to get more people to buy milkshakes in a fast-food restaurant, you need to understand the job-to-be-done for which people would come in and “hire” a milkshake. In the famous lecture below, Christensen argues that most people who buy milkshakes at a fast-food restaurant buy them because they have a long and tedious drive to work. They want something to fill their stomach while keeping the commute interesting. The milkshake does this job better than any other product. It keeps you busy for at least 10 minutes, it doesn’t crumble all over you, and you can easily keep it in your hand while steering the car.
Job-to-be-Done thinking unlocks a deeper understanding of the human behind the customer.
A while ago, we discovered in a Behavioural Design Sprint we did for a health tech company that the real Job-to-be-done for people with diabetes is to live everyday life. They want to be reminded as little as possible by their disease. People with diabetes look at every product and service through the prism of this Job-to-be-done. The unconscious question they ask themselves is: Does this product help me to approach my Job-to-be-Done to live a care-free life in which I am bothered as little as possible by my disease? This insight was crucial because, until that point, our client always communicated to people as patients.
Case: Zoku Amsterdam
The founders of Zoku Amsterdam had given themselves more than two years to figure out how they could design the ultimate hospitality experience for people who needed to stay longer in a city because of their job.
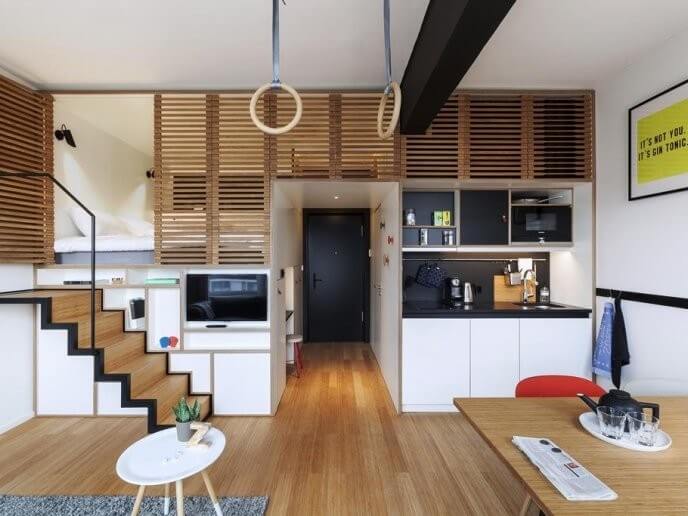

The Job-to-be-done that Zoku took as the critical opportunity for their prototyping is that people want to feel at home. They want to feel part of the community of the city. And this experience is precisely what most hotels don’t offer you. Every hotel reminds you in everything of the fact that you’re just a passenger. Zoku designed the room with this Job-to-be-done in mind. The centrepiece of the room is a dining/working table, not the bed. Lunch and dinner at Zoku are to be consumed at a long communal table. You can invite your customers for meetings, and they have daily activities in which you can participate. More about Job-to-be-Done:
Want to learn how to design behaviour?
Join our two-day Fundamentals Course and master a hands-on method to use behavioural science to develop ideas that change minds and shape behaviour.
5. The forces diagram
We already argued above that the biggest challenge with designing for behavioural change is that people need to stop doing things. Furthermore, they have all kinds of insecurities and discomfort about the new behaviour we want them to perform. We have also argued that the best way to motivate them to embrace new behaviour is to connect with their deeper goals in their life (called Jobs-to-be-done).
The third and final component of the SUE | Influence Framework© is four dynamic forces that push people towards or pull people away from the desired behaviour. The Influence Framework works with these four forces:
- Pains of the current behaviour
- Gains of the desired behaviour
- Anxieties, doubts, and other barriers to the desired behaviour
- Comforts of the current behaviour
Force 1: Pains
Pains are what people experience as shortcomings and frustrations related to their current behaviour.
Pains are often the problems to which a behavioural designer designs a solution. Pain and frustration trigger a propensity or willingness for change. The better you can connect with people’s pain, the higher the eagerness to change their behaviour.
In our behavioural design sprints, we often discover that they reward you with their trust if you can articulate people’s pain quite well. They appreciate that you understand their world. Every populist in the world knows that people are not interested in what you want to do. They want to feel instead that you get their pain. It’s a meme in every sales training that the best salesmen sell pain.
Force 2: Gains
Gains are the positive consequences that people will experience when they perform the new desired behaviour.
Whenever I stay at Zoku, I can at least work in my room if I want. I can eat healthy without having to go out. I can enjoy hanging around in the big co-working living room with my laptop. I can impress my clients with the view, etcetera. These are all gains you will experience if you book at Zoku.
However, these gains only make sense relative to the Job-to-be-Done. You appreciate the Gain of the design of your room, the shared breakfast table, the healthy food kitchen and the co-working living room because they all contribute to the Job-to-be-done of feeling at home in the city you have to stay in for work.
Important to remember: Always connect the Pains and Gains with the Job -to-be-done
Case: Pains and Gains and travelling by train
I often need to travel between Amsterdam and Belgium. I have stopped taking the car, and I only go by train these days. My Job-to-be-done is to spend my time as purposeful as possible. The Pain of driving my car is obvious: I can’t answer e-mails, write blogs, or finish reports. I’m utterly exhausted after a six-hour drive, of which I regularly spend two hours in traffic jams (Belgium is a traffic jam inferno). The Gain of travelling by train is also apparent: Travel time equals working time. I can read, write, or answer e-mails. For travellers like me, a power socket and a little table for my laptop are worth a lot.
Force 3: Comforts
Comforts are the routines and habits that get people to stick to their current undesired behaviour.
It’s not that I wouldn’t like to work out more often. And if I’m honest with myself, I do have the time to go to the gym in the morning. My only problem is that I have too many bad habits that stand in the way: I want to wake up slowly. I need to have breakfast. I need to bring my toddler to school (and she adores not cooperating). By the time I dropped her at school, my window of opportunity to go to the gym is closed. It’s already late, my stomach is full, and my mind is already at work.
You could argue that everything is in place for me to start working out. I desire to have more energy and lose a couple of kilos (my JTBD). I feel the pain of not being fit. I know how much I enjoy the feeling of being healthy (gain), and I only have to walk 200 meters to my gym, so I can’t blame it on an inability to get there. As the co-founder of SUE, I’m pretty free to decide how I run my schedule (no anxieties). I can’t break through my comforts/ habits. What works for me is that my gym organises a 10-minute abs workout every hour. If I can make it in time to join this 10-minute class, I will probably stay a bit longer.
Force 4: Anxieties
Anxieties are fears, doubts, prejudices and other barriers to the desired behaviour.
Anxieties could be all the things that prevent you from changing behaviour Anxieties could be related to:
- The desired behaviour: Too complicated, too hard, too socially uncomfortable, etc.
- The supplier: can I trust this supplier?
- My own capability: I’m not sure if I can do this or if it matches with my self-image.
- My environment: I don’t know what my significant others will think of this behaviour
Taking away Anxieties are often underestimated in a strategy for behavioural change. However, they form a crucial piece of the puzzle. Sometimes taking away anxiety is the last puzzle piece needed to turn an intervention into a success. Like in the Flixbus example I wrote about earlier: taking away my fears and prejudices towards coach travel and address the most critical force between me and the desired behaviour.
Case: De Porsche Pitch
In The Perfect Pitch, a book by advertising legend Jon Steel about the art of pitching, the author shares the story of a pitch his agency won for the Porsche account. The killer insight that got them to win the agency competition was that advertising doesn’t need to persuade Porsche drivers. It needs te to convince non-drivers that Porsche drivers are not cars for men with a middle-crisis. They called it the “asshole factor” of a Porsche driver. Taking away these anxieties and prejudices towards the Porsche driver became the most genius advertising strategy ever for the brand.
Want to shape behaviour and decisions?
Then our two-day Fundamentals Course is the perfect training for you. You will learn the latest insights from behavioural science and get easy-to-use tools and templates to apply these in practice right away!
6. Working with the SUE | Influence Framework©
The Influence Framework helps you to build empathy for your target audience. Our Behavioural Design Sprints always kick off with five or six interviews. If you interview five or six people from the target audience, you will be able to fill in your Influence Framework©. For a proper Behavioural Design interview, there’s only one simple rule of thumb:
Past behaviour never lies
When we conduct interviews, we always try to map human journeys. What we’re looking for is how real humans think, feel and behave. How does a successful journey look like? What about a failed journey? Why did people fail? What made them feel uncertain or uncomfortable? Why didn’t they do the things they wanted to do?
In 5 or 6 interviews, you’ll get a clear idea about the Jobs-to-be-Done, the Pains and Comforts of their current behaviour and the Gains en Anxieties of the desired behaviour. It can also be gratifying to interview extreme users. Experienced people can tell you a lot about Jobs-to-be-Dones and gains. People who are struggling can teach you a lot about pains, comforts and anxieties. When you have mapped out these forces, you can spot opportunities for behavioural change by asking yourself these five questions:
- How might we help people to achieve their goals? (Jobs-to-be-Done)
- Can we come up with solutions that solve pains or frustrations that people experience (Pain)
- Can we break into an existing habit? Or do we need to change a problematic habit? (Comfort)
- Which anxieties, doubts, prejudices, and other barriers do we need to take away? (Anxiety)
- What could be the psychological value that we can create for people (Gain)
More about this topic:
7. Examples
- The best way to think about the success of Uber and Lyft – aside from a nearly unlimited supply of cheap investor capital – is that they successfully eliminated all the pain from the taxi experience. Not knowing when your car is going to arrive, not being confident about whether the cabbie will rip you off or having to negotiate about the price. They brilliantly help you to achieve your job-to-be-done to experience the city. An Uber-Gain is that you never have to worry when you go out: You order an Uber when you leave the club, and within 5 minutes, you’re back on your way home.
- Airbnb is a much more gratifying way to experience new places. This is the ultimate traveller Job-to-be-done. The pain that is associated with hotels is that they’re anonymous. They make you feel like an outsider-tourist. The Gain of AirBnB on an emotional level is that you can feel at home abroad. This feeling gets even strengthened on a functional level: Since you do your cooking and supermarket shopping, you can feel what it is to live like a local. There are some anxieties Airbnb needs to take away, like whether the place is as good as advertised (that’s why they always demand professional pictures). A relatively new anxiety is the worry that the neighbourhood might be sick and tired of Airbnb tourists.
7. The ethics of Behavioural Design
We have argued above that a successful behavioural design strategy consists of three ingredients:
- A deeper understanding of human decision-making.
- Understanding the forces that shape behaviour.
- Using principles from the science of influence to come up with ideas and interventions for positive behavioural change.
The SUE | Influence Framework© is a powerful mental model for understanding why people do what they do and what prevents them from changing their behaviour. It is also the best guarantee that a strategy for behavioural change will be human-centered.
Behavioural Designers always ask themselves what they can do to help people become more successful at what they do or help them overcome their anxieties or help them break bad habits.
Suppose you take your time to build empathy with your target audience, and you use the Influence Framework to analyse their behaviour. In that case, you will always spot opportunities to design positive choices.
PS: The mission of SUE is to unlock the potential of behavioural science to help people make better decisions in work, life and play. We use this mission as our guiding principle for everything we do. We’re very conscious that behavioural design can be a ‘dark wisdom’ and that those who master it are often the ones with the worst intentions. We don’t want to be naive that people will abuse this knowledge to manipulate people. Still, we firmly believe that the world would be much better off if we can inspire more people with a better understanding of how influence works and do positive things with this knowledge. Please check out our Behavioural Design Ethics Toolkit here.
BONUS: free cheat card 'The SUE | Influence Framework© explained'
Especially for you we've created a free cheat card 'The SUE | Influence Framework© explained'. For you to keep at hand, so you can start using the insights from this blog post whenever you want—it is a little gift from us to you.
How do you do. Our name is SUE.
Do you want to learn more?
Suppose you want to learn more about how influence works. In that case, you might want to consider joining our Behavioural Design Academy, our officially accredited educational institution that already trained 2500+ people from 45+ countries in applied Behavioural Design. Or book an in-company training or one-day workshop for your team. In our top-notch training, we teach the Behavioural Design Method© and the Influence Framework©. Two powerful tools to make behavioural change happen in practice.
You can also hire SUE to help you to bring an innovative perspective on your product, service, policy or marketing. In a Behavioural Design Sprint, we help you shape choice and desired behaviours using a mix of behavioural psychology and creativity.
You can download the Behavioural Design Fundamentals Course brochure, contact us here or subscribe to our Behavioural Design Digest. This is our weekly newsletter in which we deconstruct how influence works in work, life and society.
Or maybe, you’re just curious about SUE | Behavioural Design. Here’s where you can read our backstory.









 Science as a process, behaviour as an outcome
Science as a process, behaviour as an outcome